
A complete range
of straight stems
Quadra System is a straight stem complete system for use in primary and revision surgery:
Effective stability thanks to the triple tapered design
Wide range of sizes
Reliable, compact and precise instrumentation
AMIS friendly design
Straight Cementless femoral stems have demonstrated, through 20 years clinical follow-up,
to be able to withstand biomechanical stresses by showing exceptionally good “survival rates”. [1,2,3]
With a clinical history starting in 2003 and thousands of stems implanted each year worldwide,
the Quadra System stems have proved to be a reliable solution for almost every indication of Hip Arthroplasty. [4]


Cementless stem in Titanium-Niobium alloy sand-blasting treatment.

Cementless stem in Titanium-Niobium alloy with HA (hydroxyapatite) coating.

Cemented stem in high nitrogen steel.
8 STANDARD sizes with 135° neck-shaft angle and 7 LATERALISED sizes with 127° neck-shaft angle

Cementless long stem in Titanium-Niobium alloy with HA coating.
10 sizes with 127° neck-shaft angle
The Quadra System is comprised of 2 cementless stem options sharing all mechanical characteristics, but with different surface treatments: the Quadra-S is sandblasted and the Quadra-H has an HA coating.
MATERIAL
Quadra-S and Quadra-H are made of Titanium Niobium alloy: Ti6Al7Nb. Titanium is an inert and biocompatible material ideal for direct interaction with the bone.[5,6,7] Titanium also presents the ideal stiffness for a cementless stem, avoiding stress shielding.

The surface has a superficial roughness between 4μm and 7μm thanks to a specific sand blasting treatment on the whole shaft, which allows outstanding osteointegration.[3]

The surface has an 80 μm thick HA coating on the whole shaft applied after a superficial sand-blasting. The HA coating has chemical characteristics similar to the ones of the human bone which stimulates the bony ongrowth. [8,9,10,11]
When all of the HA coating is absorbed there is good interaction between stem and bone leading to long-term stability.

SHAPE
Based on experience with straight, rectangular cementless stems.
DESIGN
Triple taper with trapezoidal cross section providing good axial and rotational stability with optimal anchoring to the bone.[12]
NECK
TAPER

PROXIMAL FEMUR
Close contact between the stem and the cortical bone thanks to the tapered shape and high precision broaches.

MACROSTRUCTURES
Horizontal and vertical macrostructures increase contact surface area by 10-15%.[13]
DIAPHYSIS

DISTAL TIP
Quadra-C is the cemented stem available with the Quadra System.


Quadra-R is a cementless straight long stem for revision purposes or pertrochanteric fractures available with the Quadra System.
It shares most of the characteristics of the cementless options:
In Titanium-Niobium alloy.
Quadra-R is available with 127° neck- shaft angle.
A dedicated instrumentation tray is available.
Quadra-R is designed from the Quadra stem, adding a longer and more important distal shaft to the stem for more distal stability in the femoral cavity.
Check stem length and neck offset for the QUADRA-R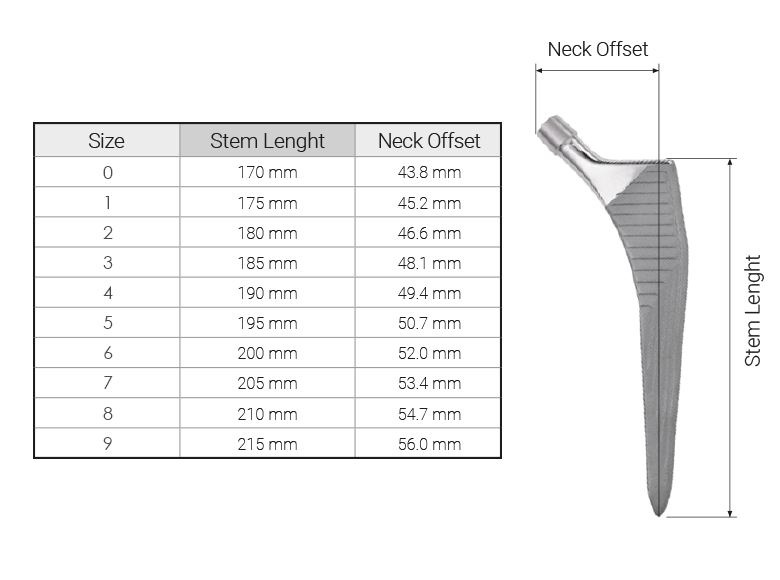

The same tray to implant Quadra-S, Quadra-H, Quadra-C*.
Both standard and lateralised trial necks fit onto the broaches for a quick and precise trial reduction.
Reliable handy manual and motorised broach handles.
Monoblock motorised broaches option available to be used with femoral stem trials.
High quality sharp broaches for a precise preparation of the medullary cavity.
Dedicated AMIS instrumentation
* Quadra-R instrumentation requires a different tray for dedicated broaches and trial necks.
AMIS is the Anterior Minimally Invasive Surgery provided and supported by Medacta International. Add one tray to have all the specific instrumentation for the AMIS approach!
Medacta, in collaboration with the surgical world, has developed a set of instruments with the aim of reducing errors, reducing the learning curve and simplifying the implementation of the AMIS technique.
You will find special retractors, reamers, cup impactor and of course special broach handles!
The AMIS Mobile Leg Positioner will be supplied as part of the instrumentation to allow a effective and reliable positioning of the leg during surgery. Traction, adduction, rotation and hyperextention have never been so easy.

[1] 20 years of Zweymüller cement free hip endoprosthesis Jatros Orthopädie - Jahrgang 5 Dez. 1999 - ISSN 0941-4770.
[2] Zweymüller K. 20 years of Zweymüller hip endoprosthesis Hans Huber Verlag 2002 ISBN 3-456-83431-4 pp 29-39.
[3] Bonnomet et al. Comportement d’une tige fémorale droite en arthroplastie totale primaire non cimentée de la hance chez les patients de moins de 65 ans Rev de Chir Orthop 2001, 87, 802-814.
[4] Cementless HA coated Quadra stem – 7 years clinical outcomes. Dr. Moreau, 2008. Data on File MEDACTA.
[5] Lintner F, Böhm G et al. Tissue Reaction to Titanium Stems. 10 Jahre Zweymüller. Verlag Hans Huber 1991.
[6] Böhm G, Lintner F et al. Morphometrical findings on individual titanium stems. 10 Jahre Zweymüller. Verlag Hans Huber 1991.
[7] Lester DK, Campbell P. 100-year-old patient with pressfit prosthesis: a post-mortem retrieval study. Am J Orthop. 1996; 25(1): 30-4.
[8] Hardy et al. Bonding of Hydroxyapatite Coated Femoral Prostheses JBJS vol 73-B, No5, Sept. 1991.
[9] Heidelberg Lab-Report, Orthopädische Universitätsklinik Heidelberg, 2005. Data on file MEDACTA.
[10] Hardy et al. Projection d’Hydroxyapatite sur Prothèses Articulaires : Progrès ou Illusion ? Acta Orthop. Bel. Vol 59, Suppl I, 1993.
[11] Fraissinet P, Hardy D et al. Histological analysis of the bone-prosthesis interface after implantation in humans of prostheses coated with hydroxyapatite. The journal of Orthop Surg. 1993; 7(3): 246-53.
[12] Data on File MEDACTA.
[13] Zweymüller K. 20 years of Zweymüller hip endoprosthesis Hans Huber Verlag 2002ISBN 3-456-83431-4 pp 11-25.
[14] Müller DA, Zingg P, Dora C. 5 year survival and radiological outcome of minimally invasive total hip replacements using a relatively new implant (Quadra/Versafitcup, Medacta, Switzerland). SGO 2011, 22th-24th June, Lausanne